حذف برنامه های پیش فرض گوشی
Android SDK Platform Tools download is now available as a zip file directly from Google. Just download the latest SDK platform-tools zip containing ADB and Fastboot binaries for Windows, Mac, and Linux from below and unzip it. You can then be able to execute ADB and Fastboot commands to install APK, reboot your Android into the bootloader mode and flash stock ROM and recovery images using your Windows, Mac or Linux or Ubuntu computer.
The Android SDK and Android Studio are tools for developers only and they are used for Android application development purposes. However, if you are just a nerd who messes around your phone for smaller jobs like unlocking the bootloader, flashing boot or recovery image or the full factory images occasionally, downloading the full Android SDK or Studio is no more necessary. You can now download the latest ADB and Fastboot tool or Android SDK Platform-Tools zip file depending on your computer’s OS separately.
Platform-Tools is a component of the Android SDK and it includes different tools, such as ADB, fastboot, and systray. If you have ever wanted to download ADB and Fastboot without having to download the whole of Android Studio or SDK, Google has finally made those binaries available officially for Windows, Mac, and Linux. Thus you can now download the latest ADB and Fastboot files from Google Developer site.
Before this new development, users had to download Android SDK or Studio, which are a 400MB to 1.6GB download, and rely on 3rd-party sources to grab the ADB and Fastboot drivers. You must be familiar with Minimal ADB and Fastboot executable that we needed to install to get the Android SDK Platform Tools.
In many cases, the 3rd-party downloads contain malicious stuff like Trojans. Furthermore, to get the latest SDK platform tools, we had to keep an eye on the new releases. Sometimes the latest version of such executable tools installs the outdated ADB and Fastboot binaries. It’s time now to get rid of the middlemen and get the latest tools straight from Google.
Read Also: How to Setup ADB and USB drivers on Ubuntu
Why download a giant package of junk if you need just a small chunk? The size of the official Platform Tools is less than 4MB.
Download Android SDK Platform Tools
SDK Platform Tools for Windows
platform-tools-latest-windows.zip
ADB Platform Tools for MacOS
platform-tools-latest-darwin.zip
SDK or ADB Platform Tools for Linux and Ubuntu
platform-tools-latest-linux.zip
You can also visit the official page and take a look at the release note. If you want to use your Android phone like a PC for executing ADB and Fastboot commands, please read out guide on the topic.
Useful Tip: How to Hide Root on Android and Pass SafetyNet Check
Steps to Use and Execute ADB Commands
Having downloaded the latest SDK Platform-Tools.zip file, just extract it on your desktop. Open the extracted folder, and launch a command window inside the “platform-tools” folder and execute the desired ADB and Fastboot commands.
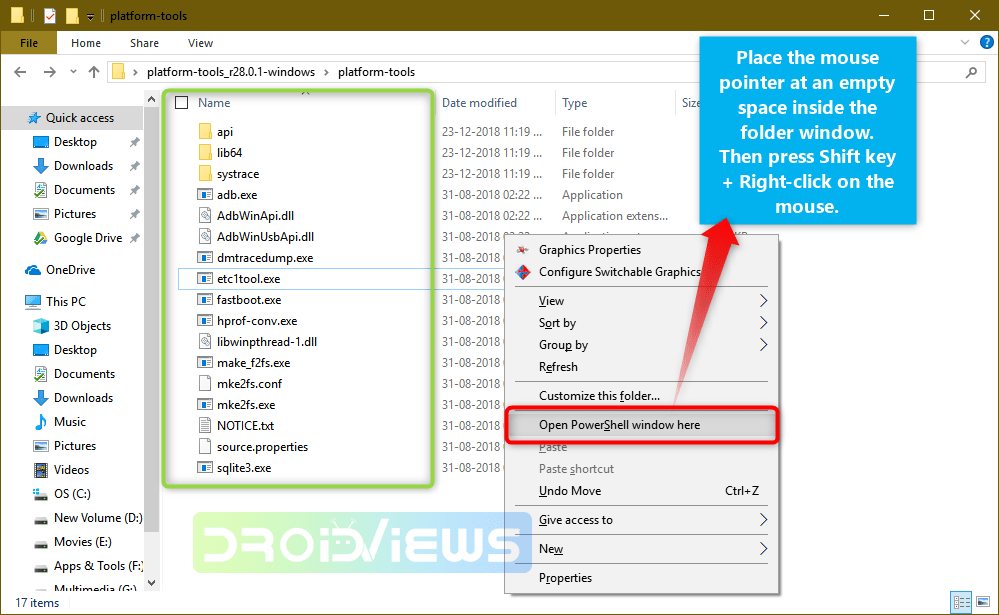
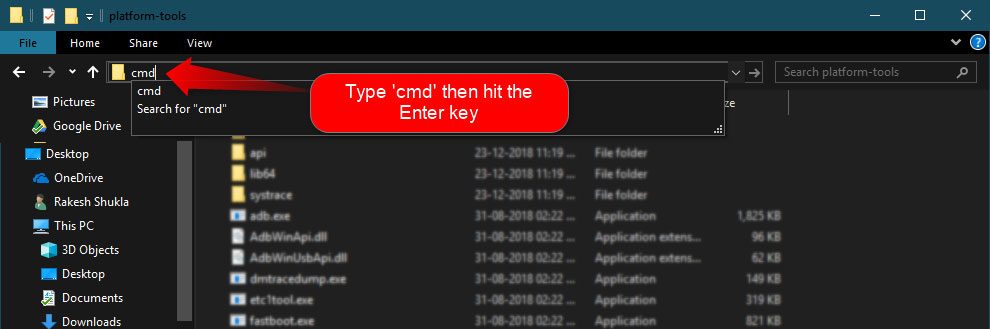
There are two ways to open the command window from a folder window. The easiest and quickest way to launch the command or cmd prompt window from the platform-tools folder window is to type “cmd” in the window address bar and hit the Enter key.
You can also open a command prompt on Windows as follows. Pace the mouse pointer at any empty space inside the folder, then press Shift key+ Right-click on the mouse and select “Open command window here” or “Open PowerShell window here” (on Windows 10) option.
Having launched the CMD window, you can execute ADB or Fastboot commands.
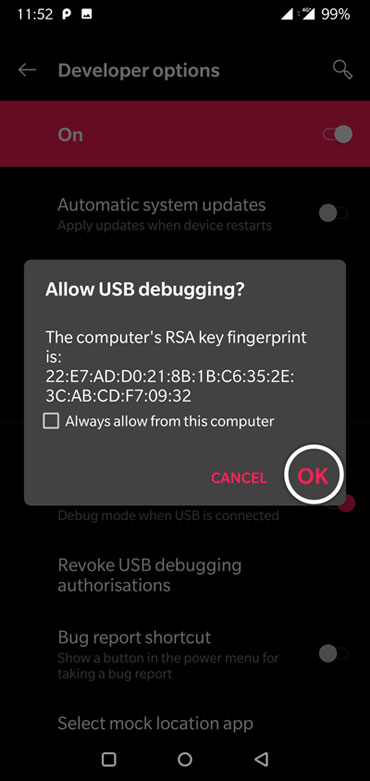
Don’t forget to authorize ADB and allow USB debugging on your Android device when prompted. Also, to be able to use ADB and Fastboot commands, you must enable USB debugging on your device.
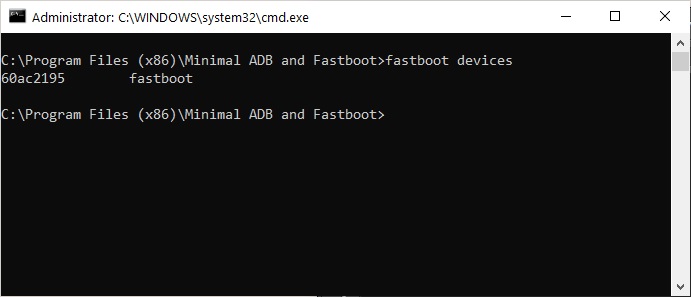
For instance, if you want to check the connection between your Android device and computer, you can try the following command:
adb devices
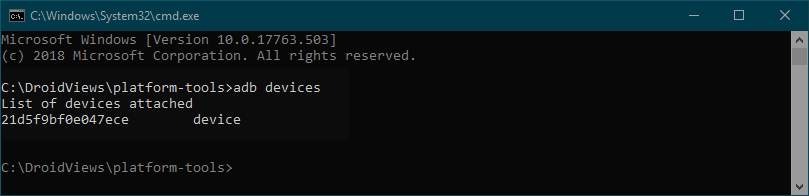
Similarly, you can reboot your Android device into the Bootloader mode using “adb reboot bootloader” command and even install an APK app. Do not forget to check out the full list of ADB and Fastboot commands.
ADB Commands List
As mentioned earlier, ADB commands are used when the device is powered on and you have access to the device. That is, you can unlock the device and grant ADB debugging permission to the computer. Listed below are some of the most common and useful ADB commands that you may need at some point. You can even use your Android phone like a PC to execute ADB and Fastboot commands.
adb help
Displays the Help Documentation on ADB commands.
adb devices
Shows all the devices connected to ADB. Can be used to make sure your device is connected properly before performing any other operations.

adb usb
It shows all Android devices and emulators connected to your computer via a USB cable.
adb devices //show devices attached
This command will display the list of all Android devices attached to your PC.
adb connect ip_address_of_device
Using the ‘adb connect’ command, you can connect the IP address of your Android device to your computer.
adb reboot
ADB can be used to reboot your device, useful when your hardware buttons aren’t working or if you’re already using ADB. You can also reboot directly into the recovery or bootloader using this command.
adb reboot bootloader
Reboots the device into the Fastboot or Bootloader mode.
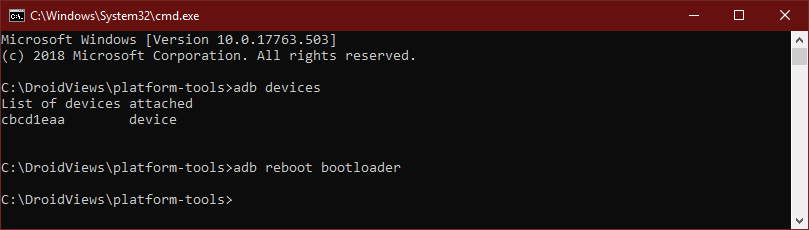
adb reboot recovery
Reboots the device into recovery mode.
adb install
It can be used to install an APK file on your Android device from your computer. It is more convenient than the alternative, which is to transfer the APK to the device and then install it. This command is generally used by developers or debuggers. Please note that you must copy the APK file to install in the ‘platform-tools’ folder, otherwise you’ll also have to type the location of the APK.
adb install OPLiveWallpapers.apk
Use the following command to re-install or update an existing app on your device and keep its data.
adb install -r OPLiveWallpapers.apk
If the app (APK) you are installing supports move to SD card feature, you can install it to the SD storage using the following command.
adb install -s OPLiveWallpapers.apk
adb install –k <.apk file path on computer>
Below are some more parameters that can be used with the ‘adb install’ command:
adb -e install path/to/app.apk
-d (directs command to the connected USB device.)
-e (directs command to the running emulator.)
-s<serial number>
-p <product name or path>
adb uninstall
This command can be used to uninstall an installed app, which is pretty clear from the command itself.
adb uninstall com.facebook.katana
Use the following command if you want to uninstall an app package but keep its data and cache directories.
adb uninstall -k com.facebook.katana
Keep the data and cache directories around after package removal.
adb logcat
Displays the log data onto the screen. You can use this command with the following parameters for different purposes as shown below.
adb logcat -c // clear //
By adding the ‘-c’ parameter to the ‘adb logcat’ command, you can clear the existing logs on an Android device.
adb logcat -d > [path_to_file] //
Similarly, by using the ‘-d’ parameter, you can save the logcat output to a file on your computer.
adb bugreport
Displays the Android device information such as dumpsys, dumpstate and logcat data on the screen.
adb jdwp
Lists the JDWP (Java Debug Wire Protocol) processes on the device. if you’re not already aware of it, chances are you don’t have to worry about it either.
Don’t Miss: 50 Best Apps for Rooted Android Devices
adb get-serialno
Displays the adb instance serial number string with the device.
adb get-state
Shows the status of the device.
adb wait-for-device
This command is used to program delay before the next command is issued. It executes when the device is online but it can be programmed to wait till another process is done.
adb start-server
Starts the adb server process.
adb kill-server
Stops the adb server process (terminal adb.exe process).
adb sideload
Just as you can flash zip packages from a custom recovery, you can also do it via adb sideload, provided the recovery supports it. TWRP recovery which is the most common custom recovery for all devices does support it. This way you can flash packages directly from your computer without having to transfer them first to your device or any external storage.
To sideload a mod or update.zip file successfully, you must copy it first to the SDK folder.
adb sideload sample.zip
adb pull
This command can be used to pull any files from your device and save it on your computer. To download or pull a file from your Android device to the SDK platform-tools directory, use
adb pull /sdcard/screenrecord.mp4
If you want to download a file from your phone’s storage to a specific drive on your computer, execute the following command
adb pull /sdcard/screenrecord.mp4 e:\
adb push
Similarly, this command can be used to push a file from your computer to your device. If the file to be pushed it save in the SDK folder, use
adb push OPLiveWallpapers.apk /sdcard
To push or send a file to your Android from a specific drive on your computer, use
adb push e:\OPLiveWallpapers.apk /sdcard
Having given you the above ADB commands list, let’s check out the ADB Shell commands list below.
adb backup //
By using this ADB command, you can create a full backup of your Android device and save to your computer.
adb backup //
adb restore //
Use this command to restore a backup to your device.
adb restore //
ADB Shell Commands List
Below is the list of some really useful ADB shell commands.
adb shell
The ‘adb shell‘ command starts the remote shell command console in the device and lets you control the device through it.
adb shell pm uninstall -k –user 0
You can uninstall or remove any system app installed on your Android device. This is the easiest way to uninstall bloatware. Just use the following command followed by the app package name.
pm uninstall -k –user 0 com.facebook.katana
Learn more about debloating Android devices without root in our dedicated article.
adb shell dumpsys
You can use this ADB shell command to dump all system data about your Android device’s hardware and software configuration.
adb shell dumpsys
You can also use it to get information about specific components of your device, such as display, battery, etc.
adb shell dumpsys display
adb shell dumpsys battery
adb shell dumpsys batterystats
adb shell wm density
This command allows you to change the pixel density of your Android device’s display without any hassles. In order to change your Android phone’s screen resolution, you must know its original resolution. If you don’t know that, execute the following command:
adb shell dumpsys display
Issuing the above command for the Galaxy S9+ gave me the following info about my phone’s display resolution and density.
mDisplayInfos= PhysicalDisplayInfo{1440 x 2960, 60.000004 fps, density 3.5, 530.086 x 529.464 dpi
Now, if I want to set a lower resolution for my Galaxy S9+, I’ll use the following commands. This value can vary per phone, you’ll know it’s right when you can read text and apps don’t render too small value is from 120 up to 640
for 1080p (FHD)
adb shell wm size 1080×2220
adb shell wm density 480
for 720p (HD)
adb shell wm size 720×1560
adb shell wm density 350
adb shell pm list packages
The following commands print the names of all app packages installed on your Android device. You can add additional conditions or filters to list specific packages only.
To list all packages:
adb shell pm list packages
To get a list only system packages
adb shell pm list packages -s
To list only 3rd-party packages
adb shell pm list packages -3
To show only the disabled app packages:
adb shell pm list packages -d
To show only enabled app packages
adb shell pm list packages -e
To list uninstalled app packages with installed pages.
adb shell pm list packages -u
ADB Shell command to Send SMS screen
By sung this command, you can send the text message screen with the message content and phone number.
adb shell am start -a android.intent.action.SENDTO -d sms:+919792211100 –es sms_body «Test –ez exit_on_sent false
adb shell screencap
By using the following ADB shell commands, you can capture the screenshot of your device display and then download the captured screen to your computer.
adb shell screencap /sdcard/screenshot.png
adb pull /sdcard/screenshot.png
adb shell screenrecord
On Android devices running Android 4.4 KitKat and above, you can even record your phone or tablet’s screen and download the recorded video to your computer using the ADB shell commands. Besides, you can also set conditions like video duration, resolution in pixels and video bitrate, etc. You need to press Ctrl+C to stop recording manually.
adb shell screenrecord /sdcard/screenrecord.mp4
adb pull screenrecord /sdcard/screenrecord.mp4
Use the following command to set the width x height of the video:
adb shell screenrecord –size 1920×1080 /sdcard/screenrecord.mp4
By default, Android’s screen recorder’s duration is set to 180 seconds (3 minutes). You can decrease this time limit according to your needs (180 seconds is the maximum limit).
adb shell screenrecord –time-limit 120 /sdcard/screenrecord.mp4
Similarly, you can also determine the bitrate of the video output. To set the bitrate to 4MBPS, for example, you can use the following value:
adb shell screenrecord –bit-rate 4000000 /sdcard/screenrecord.mp4
adb shell cd
Change ADB shell directory using ‘cd <directory>‘
adb shell (Hit Enter then the following command) cd /system
adb shell rm
By using this ADB shell command, you can remove any file or directory from your Android device.
To do that, you have to type ‘adb shell‘ command first and hit the Enter key. After that, you can use one of the following commands followed by the file or directory name as shown below.
Delete a file:
rm -f /sdcard/OPWallpaperResources.apk
Delete a directory or folder:
rm -d /sdcard/ZooperWidget
You can also use ‘rmdir‘ in place of ‘rm -d‘ to remove a directory.
adb shell mkdir
This ADB shell command is used to create a new directory or directories under an existing directory. You can also set permission for the directory too. Execute ‘adb shell’ and then the following commands:
mkdir /sdcard/NewFolder
mkdir -m 644 /sdcard/NewFolder
mkdir -p /sdcard/NewFolder/Folder1
adb shell cp & adb shell mv
You can use these commands to copy, move and rename files and directories. Again, you need to start with the ‘adb shell‘ command first.
To copy files and then paste them, by mentioning the source and destination locations as shown below:
cp /sdcard/OPWallpaperResources.apk /sdcard/LiveWallpapers
To move a file from one location to another, type the following command mentioning the source and destination locations:
mv /sdcard/OPWallpaperResources.apk /system/app
If you want to move a file to a different location with a new name,
mv /sdcard/OPWallpaperResources.apk /sdcard/OPLiveWallpapers.apk
adb shell netstat
To check the network statistics of your Android device, execute ‘adb shell‘ command and type:
netstat
adb shell ip
Using this command, you can see, your phone’s Wi-Fi IP address. Execute ‘adb shell‘ in the command window and then issue the following command:
ip -f inet addr show wlan0
adb shell top
If you want to know about the top CPU processes running on your Android device, you can use the following command after executing ‘adb shell‘:
top
If you want to stop CPU processes monitor, press Ctrl+C on your keyboard.
adb shell getprop & adb shell setprop
Using the above commands, you can not only get the properties of your Android’s build.prop configuration but can also set a value of property tag on the build.prop. See the examples below:
Type ‘adb shell‘ in the cmd window, hit the Enter key and then issue the following command:
getprop
Below are some more examples:
getprop ro.build.version.sdk
getprop ro.chipname
Now, to set the value of a specific build.prop property, you can use the ‘adb shell setprop‘ commands. See the examples below:
setprop net.dns1 1.2.3.4
setprop net.dns2 1.2.3.5
Similarly, you can also set a custom VMHeap size:
setprop dalvik.vm.heapsize 40m
ADB Shell KeyEvent commands
By using the following ADB Shell key event commands, you can trigger certain actions performed by certain hardware buttons or UI options on Android devices.
adb shell input keyevent 3 // Home btn
adb shell input keyevent 4 // Back btn
adb shell input keyevent 5 // Call
adb shell input keyevent 6 // End call
adb shell input keyevent 26 // Turn Android device ON and OFF. It will toggle device to on/off status.
adb shell input keyevent 27 // Camera
adb shell input keyevent 64 // Open browser
adb shell input keyevent 66 // Enter
adb shell input keyevent 67 // Delete (backspace)
adb shell input keyevent 207 // Contacts
adb shell input keyevent 220 / 221 // Brightness down/up
adb shell input keyevent 277 / 278 /279 // Cut/Copy/Paste
Learn more about tweaking VM heap size to improve Android’s performance.
Fastboot Commands Lists
These commands can be used only when the device is in the Fastboot mode. You can try a button combination to put your device into this mode or use the ADB command mentioned above.
adb reboot bootloader
Once in Fastboot mode, you can use a number of Fastboot commands as mentioned below.
fastboot devices
Displays all the connected devices. Can be used similarly as the ‘adb devices’ command to make sure the device is properly connected.
fastboot oem unlock
Unlocks the bootloader on some Android devices such as Pixel or OnePlus. Most other Android devices require you to get an unlock key from the OEM.
fastboot oem lock
Used to relock the bootloader of your device.
fastboot reboot bootloader
Reboots the device from the fastboot mode back into fastboot mode. Sometimes this may be necessary when you’re flashing things in the fastboot mode.
fastboot flash
This command can be used to flash things onto your device. This can be a zip file, a boot image or a recovery image.
fastboot flash boot boot_image.img
Flashes a boot image to your device.
fastboot flash recovery recovery_image.img
Flashes a recovery image to your device.
fastboot boot image_file.img
This command can be used to boot your device using a certain image file without having to flash it first. Can be useful to test an image before flashing it. Should you have any questions about Fastboot commands, please let us know.
So, here end our list of useful ADB and Fastboot commands that can help Android users perform a plethora of commands using cmd. Let’s know if we forgot to mention any command that should have been our list.
برگرفته سایت droidviews.com